Basics of Search Engines and Why You Should Care?
In today’s time, search engines like Google, Bing, Yahoo, etc., have become an integral part of the daily lives of students, professionals, business owners, homemakers, unemployed youths, or even senior citizens alike. We all search for answers to our queries on search engines, ranging from places to dine, places of worship, or doctors nearby, or gyms or shopping and what-not. But have you ever wondered how you get answers almost instantly to the queries? The simple answer to this is that search engines crawl the indexes and provide you with the relevant results.
It may sound a bit complicated as it is complicated. Robots called bots or spiders crawl billions of pages to extract the most relevant results for every search query.
Therefore, if you are an entrepreneur, a blogger, or associated with a profession that needs Search Engine Optimisation or Search Engine Marketing, you must know how Search Engines like Google, Bing, etc., work.
To bring more traffic to your website or web pages, you need to follow specific parameters to rank higher in the search results. And in turn, you need to be indexed and visible to the search engines to show higher on the result pages. This visibility is arguably the most critical piece in the SEO Puzzle: If you aren’t indexed and visible, then there’s no way you will ever show up in SERPs (Search Engine Results Page).
So, to make you familiar with these aspects of search engines, we will discuss the following:
- Basics of search engine
- Index building by search engines
- Page ranking process
- Approach of personalized search results
Let’s delve deeper into the above points
1. Basics of Search Engine
Before jumping into the technicalities, let’s first understand what search engines are, why they exist, and why we must even care to learn about them.
What are Search Engines?
Simply speaking, search engines are tools to get answers to the user’s queries through searching the web contents.
Every search engine consists of two main parts:
Search index – A digital library about web page information.
Search algorithms – Computer programs help ranking matching results from the search index.
Few famous examples of search engines are Google, Bing, Yahoo, DuckduckGo, etc.
The goal of search engines
Every search engine strives to provide the best, relevant, and most popular results to users. More the relevance, the more the market share.
How does the search engine make money?
Search engines provide two types of results:
Organic search results are from the search indexes. This cannot be paid for.
Paid search results are the Ads that you can pay for to be visible.
Every time a user clicks on the displayed ads, the advertisers pay the search engines. This is called pay-per-click advertising.
Here comes the market-share and popularity in play. More users mean more revenues for the search engines.
Why should you care about the way search engines work?
Familiarity with the process of search engine functions will help you get more organic traffic to your websites for free. If you suffice the ranking factors, your page will be displayed in higher positions of the search results, compelling the users to click your links and that will establish more authority of the site.
Most popular search engine
Google is the most popular search engine with a 92%+ market share. After Google, the next biggest search engine is YouTube.
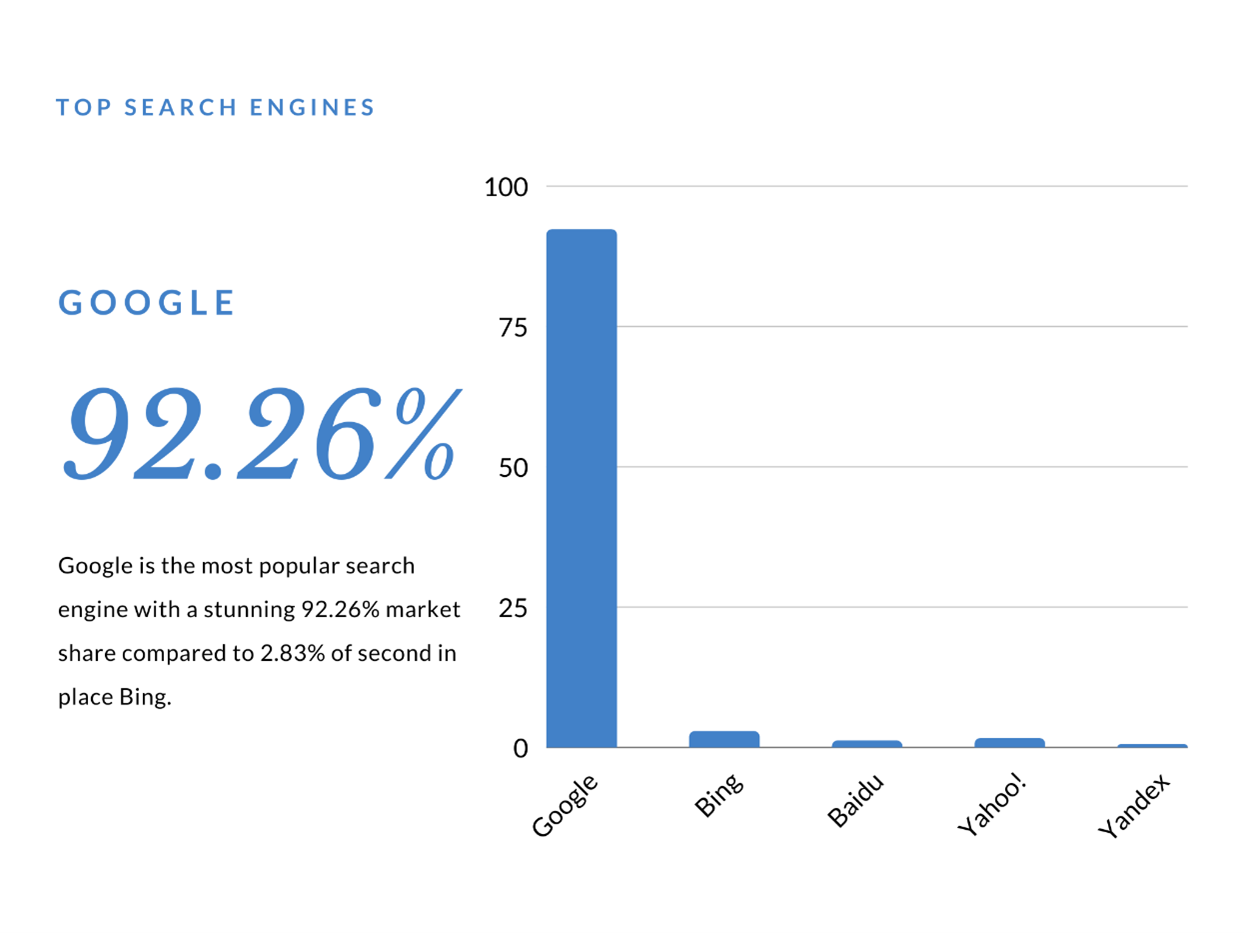
Google has the highest user base. Hence, it is on the list of every SEO professional and website owner to become relevant to Google parameters for getting traffic. If you want to rank your videos, you need to know the techniques of increasing YouTube subscribers and expanding your reach.
2. Index building by search engines
Index building is the most crucial attribute for any search engines’ success. Well-known search engines like Google crawls through trillions of pages to provide the most fitting response.
As per Google, the process of indexing has four steps:
Step 1: URLs
Step 2: Crawling
Step 3: Processing & rendering
Step 4: Indexing
Although here we are describing the system used by Google, almost all other search engines follow similar processes.
Step 1: URLs
Everything begins with the URLs. Google searches for URLs through various processes. The most common ones are the below-mentioned three ways.
Through Backlinks: In the index of Google, there are already trillions of pages available. If someone links one of those pages to one of your pages, Google can find you through that link. These links help discover newer pages, images, documents, and websites, both by humans and search engines.
Through Sitemaps: All the pages of your website are listed on Sitemap. Once you submit your sitemap to Google, your website may be discovered faster.
From submissions of URLs: Google allows submissions of individual URLs via Google Search Console.
Step 2: Crawling
To gather information, Google uses computer programs called crawlers or spiders. These bots search the internet to find the servers to accumulate and download relevant pieces of information.

But it is noteworthy to mention that Google doesn’t always crawl pages in the order it discovers them.
Instead, Google signals URLs for crawling based on certain factors, including:
- URL’s PageRank
- Frequency of URL changes
- Newness of the URL
So, if you have a large website, it might take some time for Google to crawl all the pages as it may discover few pages before others.
Step 3: Processing & rendering:
In this step, Google performs tasks to understand and extract critical information from the crawled pages. It is unknown how the details are processed, but the vital factor remains drawing out the links and to store the results for indexing.
Google has to render the pages to fully process them, which is where Google runs the page’s codes and checks its bearing for the users.
Step 4: Indexing:
Once the whole process of crawling, processing, and rendering is completed, the assembled information needs to be organized, sorted and stored. In this way, they can be processed by Google’s algorithms before being made available to the users.
This organizing is called indexing. An index is essentially a digital library where trillions of pages are stored in the database. Google results come from this database.
Therefore, it is interesting to mention that when you search the internet for any queries on Google, you are not getting the results from the internet, but from this vast database that Google maintains.
3. Page ranking process
Once the discovering, crawling, and indexing content processes are over, the ranking of the page process begins. This PageRank is done through various algorithms used by Google, as many as 200+ in numbers.
Out of this many algos, the key factors are as below:
- Inter-linking
- Relevance
- Freshness
- Topical authority
- Page speed
- Mobile-friendliness
Inter-linking: Just like the crawlers use URLs and links to discover your site, you need to provide links to various pages in your own website to become visible to the crawlers. If you don’t create a proper path of being seen by the crawlers inside your own website, it is as good as invisible.
However, not all links are equally perfect for being discovered by Google. Features like relevance, authority, anchor text, follow vs. no-follow, placement, and destination create good backlink.
Of these, authority and relevance are the most critical ones.
Tools like ahrefs can provide an insight on the authority of the Domain Rating (DR) and URL Rating (UR)
Link Relevance means links from similar websites are most beneficial. Google talks about relevance in the context of ranking valuable pages on its page about how Google search works.
Relevance: Google uses a variety of algos to establish page relevance. Most basic seems to be keywords searched by the users. But it also uses user interaction data to assess the final intent.
For example, if your search query has “Apple” as a keyword, you can get results for both the fruit and the mobile company. But if your past interactions were for things like iPhone, iOS, or iPad related, you will most likely see the “Apple” mobile company as top results.
Freshness: Freshness is a question-reliant deciding factor. If someone wants to know about the current President of the USA, the answer will be according to the time asked for.

But if someone asks for an American pie recipe, here the freshness is less relevant.

Whereas, for things like “how to tie a tie”, here the freshness is altogether irrelevant.

Topical authority: A topical authority is the deemed authority on any niche as opposed to a singular term or idea. Meaning, Google might view your page for one suggestion but not another.
This is probably why Google’s SEO starter guide tells website owners to cultivate a reputation for expertise and trustworthiness in a specific area.
Page speed: Page speed is determined by how fast an answer page loads after you search for a query. Google knows this well that nobody likes to wait longer for a page to load. In the year 2010, they decided to make speed a factor of ranking your page in the desktop version, and in 2018, for the mobile searches.
Google’s PageSpeed Insights can provide you with solutions to fix it if it is slower than expected by Google.
Mobile-friendliness: 65% of Google searches happen on mobile devices. Hence, since 2015, it has become one of the critical factors for PageRank. Since 2019, when Google switched to mobile-first indexing, mobile-friendliness also became essential for desktop searches. Google predominantly uses mobile-friendliness as a ranking factor on all platforms.
4. Approach of personalized search results
Whenever you search for answers about any specific topic, have you noticed how personalized the responses you get? This happens because search engines like Google know that different results appeal differently to other people. And the results, too are tailor-made to suit your specific needs.
Google states that “information such as your location, past search history, and search settings all help us to tailor your results to what is most useful and relevant for you at that moment.”
Let’s understand them one by one.
Location: If you search for something like “Italian Restaurants,” you will see results of all the local restaurants in your area. This is because of apparent reasons; Google knows that you are very unlikely to travel halfway around the world for lunch.
It is similar to any search like “best salon nearby” or “medical stores”. The results are always customized as per the locality we search from.
Language: Google understands the cultural and language preferences of the population. Hence, if you are in France, results will come in French instead of English. To cater to this variety, Google translates pages in more than 110 different languages.
However, Google is reliant on the website owners for this translation. So it would be appropriate if you suggest to Google about the multi-language availability of your content.
Search history: The most obvious example of personalization based on search history by Google is the change in the ranking of a page based on past searches. Once clicked links and pages rank higher in the search results for repeated queries.
Closing bells
Knowing how search engines, specifically Google works, will help you rank better and garner more organic traffic. If search engines do not discover, crawl or index your website, then you are as good as a fish out of water.

